Pneumatics Item
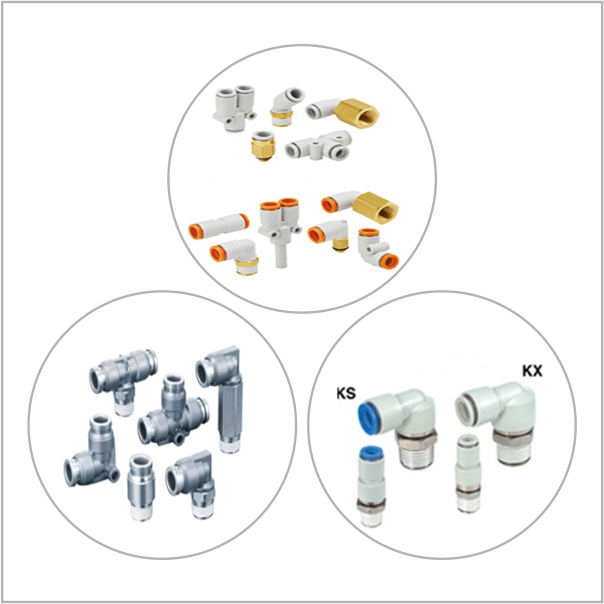
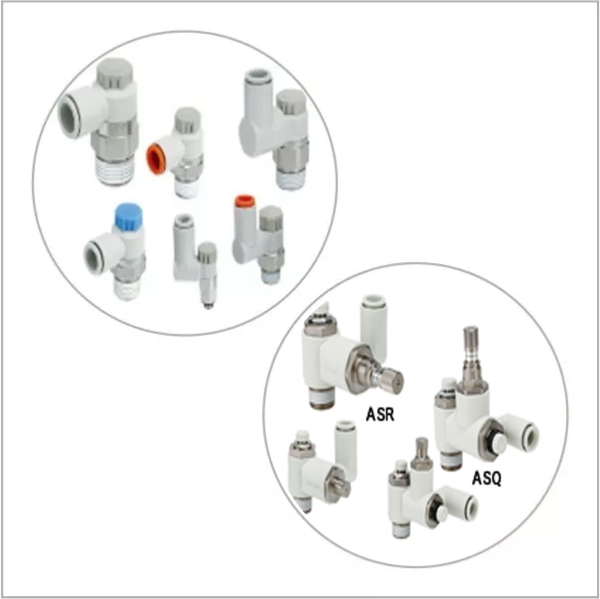
Pneumatic Items
Pneumatic systems utilise compressed air to perform work, making them vital in many industries, including manufacturing and automation. These systems are praised for their speed and reliability, allowing for quick operation in various applications, such as powering tools, controlling machinery, and moving materials.
One of the key advantages of pneumatic systems is their cleanliness. Unlike hydraulic systems, which use oil and can create spills or leaks, pneumatic systems produce minimal pollutants, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
Types of Pneumatic Components
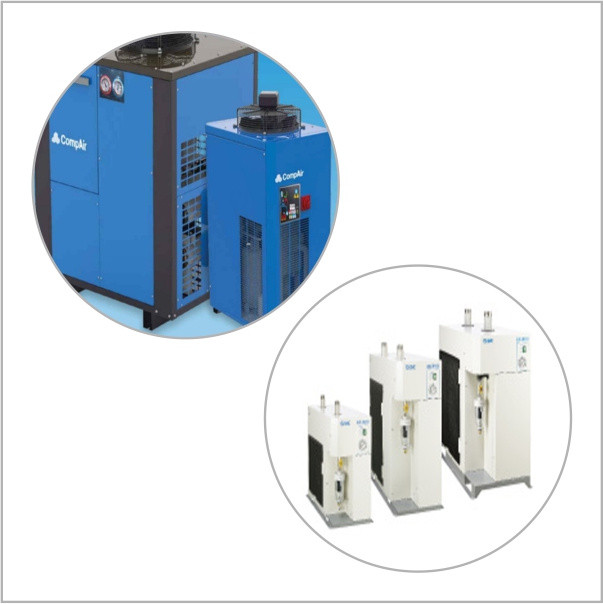
- Compressors: These devices generate compressed air by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, which pressurises the air. They are the heart of any pneumatic system, providing the necessary air supply.
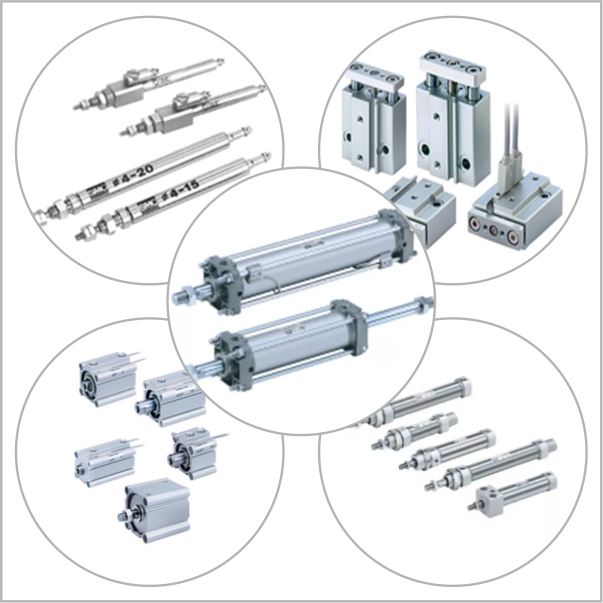
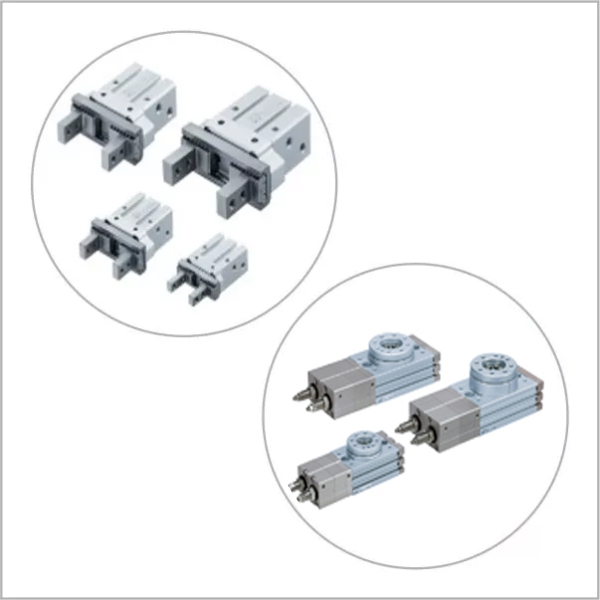
- Actuators: Actuators convert the energy from compressed air into mechanical motion. Common types include cylinders, which create linear movement, and rotary actuators, which provide rotational motion for various applications.
- Valves: Valves control the flow and direction of compressed air within the system. They can be manual or automatic and are essential for regulating pressure and ensuring safe operation.
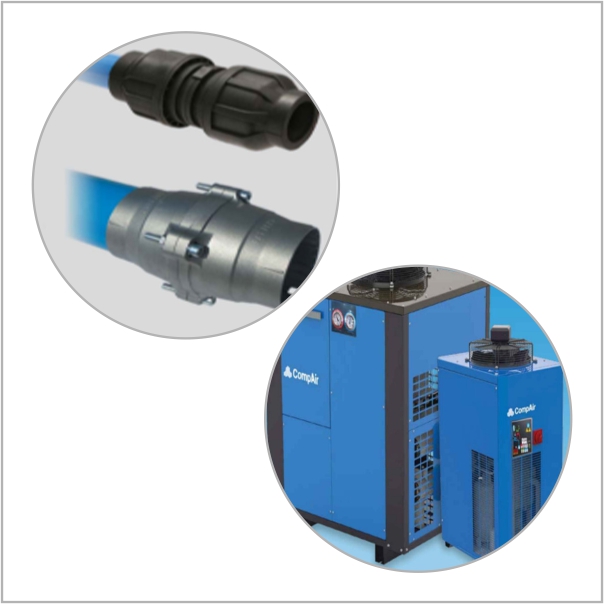
- Hoses and Tubing: These components transport compressed air from one part of the system to another. They come in various materials and sizes to accommodate different pressure levels and application needs.
Pneumatic systems are made up of several key components, each serving a specific function to ensure efficient operation:
It is important to understand these pneumatic components are crucial for designing, maintaining, and optimising pneumatic systems, ensuring reliable and efficient performance in industrial applications.
Applications of Pneumatic Technology
- Packaging: Pneumatic systems are used in packaging machines to handle and seal products efficiently. They can operate quickly and precisely, ensuring consistent packaging quality.
- Material Handling: Pneumatic tools, such as conveyors and lifts, facilitate the movement of materials within a facility. This automation helps streamline workflows and reduce manual labor, enhancing productivity.
- Assembly Lines: In manufacturing, pneumatic actuators and tools are commonly employed on assembly lines for tasks like fastening, gripping, and positioning components. This automation allows for high-speed production and reduces the risk of human error.
- Automotive Industry: : Pneumatic systems power tools like impact wrenches and spray guns, providing the necessary force for tasks such as painting and assembly while ensuring worker safety and efficiency.
Pneumatic technology is widely utilised across various industries due to its versatility and effectiveness. Some common applications include:
The versatility of pneumatic technology makes it an invaluable asset in processes that require repetitive motions, significantly improving productivity and safety in the workplace.
Maintenance Tips for Pneumatic Systems
- Check for Leaks: Regularly inspect hoses, fittings, and connections for any signs of air leaks. Even small leaks can lead to significant efficiency losses and increased energy costs.
- Ensure Proper Lubrication: Keep all moving parts well-lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Use the appropriate lubricant and follow manufacturer guidelines for frequency and application.
- Inspect Components for Wear: Regularly examine components such as actuators, valves, and filters for signs of wear or damage. Timely replacement of worn parts can prevent system failures and improve performance.
- Clean Filters and Regulators: Keep air filters and pressure regulators clean to ensure optimal airflow and pressure control. Clogged filters can restrict air supply and affect system efficiency.
- Conduct Routine Testing: Perform periodic testing of system pressure and flow rates to identify any deviations from normal operating conditions. This can help catch potential issues early.
Regular maintenance is essential for pneumatic systems to ensure they operate efficiently and reliably. Here are some key practices:
By following these maintenance tips, you can reduce downtime, extend the lifespan of your pneumatic system, and ensure optimal performance in your operations.
Future of Flow Measurement
The flow measurement industry is rapidly evolving due to advancements in technology. Smart flow instruments equipped with IoT capabilities are becoming increasingly popular, allowing for remote monitoring and real-time data analysis. These devices enable predictive maintenance, which helps identify potential issues before they lead to failures, thereby minimising downtime and reducing operational costs.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is enhancing data interpretation, allowing for better forecasting and process optimisation. Advanced analytics can identify patterns and trends in flow data, helping businesses make informed decisions that improve efficiency.
There is a growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency. New flow measurement technologies are designed to optimise resource usage, reduce waste, and lower energy consumption.
For example, advanced flow meters can help manage water usage in agricultural applications, contributing to more sustainable practices.
As these innovations continue to emerge, we can expect increased automation, improved accuracy, and enhanced safety in flow measurement, leading to smarter, more efficient operations across various industries.
The Future of Pneumatics: Innovations and Advancements
- Smart Sensors: These devices enable real-time monitoring of pressure, flow, and temperature, providing valuable data that can be used for predictive maintenance and troubleshooting. This leads to enhanced reliability and performance.
- IoT Integration: By connecting pneumatic systems to the Internet of Things (IoT), operators can remotely monitor and control systems from anywhere. This integration allows for improved data analysis and decision-making, optimising operations and reducing costs.
- Advanced Automation: New technologies are facilitating more sophisticated automation solutions, allowing for seamless integration with other automated systems in manufacturing and production environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Innovations focused on energy-saving technologies are helping to reduce the carbon footprint of pneumatic systems, making them more environmentally friendly.
These advancements are paving the way for more efficient, reliable, and sustainable pneumatic systems, ensuring they remain a key component in modern industrial applications.
As technology continues to evolve, pneumatic systems are becoming increasingly smart and efficient. Innovations like smart sensors and IoT integration are revolutionising how these systems operate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What Are Pneumatic Items?
Pneumatic items are components and systems that use compressed air to perform mechanical work, commonly used in tools and industrial applications. - What Are the Main Components of a Pneumatic System?
Key components include air compressors, actuators (such as cylinders), valves, and hoses that work together to control the flow of compressed air. - What Are the Benefits of Using Pneumatic Systems?
Pneumatic systems offer benefits like speed, precision, cleanliness, and lower energy costs compared to hydraulic systems, making them ideal for many applications. - How Do I Maintain My Pneumatic System?
Regularly check for air leaks, clean and lubricate components, and perform inspections to ensure all parts are functioning correctly. - What Industries Commonly Use Pneumatic Technology? Pneumatic technology is prevalent in manufacturing, automotive, food processing, and packaging industries, among others, where automation and efficiency are critical.